IB HSC Physics Doppler Effect for Sound
/A tutorial sheet of Doppler effect questions for sound is given below.
- The speed of sound in still air is v. A train blowing its whistle is moving to the east at a speed vs. What is the speed of sound at a point (a) east of the train, (b) north of the train, (c) west of the train, (d) south of the train.
- When a source of sound waves moves towards you do you measure an increase or decrease in the speed of the waves?
- When the moving source emitting sound waves is directly opposite the observer is there an observed frequency shift in the sound? [no]
- A train sounding its whistle moves to the east at a speed vs. An observer moves at a velocity vo towards the train. Is the observed frequency the same as the case when the observer is at rest and the train is approaching at a speed vs+vo?
- Draw the wave pattern when (a) vs < v, (b) vs = v and (c) vs > v. In the last case show the bow wave.
- A car traveling at 10 m/s sounds its horn, which has a frequency of 500 Hz, and this is heard in another car which is travelling behind the first car in the same direction at 20 m/s. The sound can also be heard in the second car by reflection from a bridge. If the speed of sound in air is 340 m/s what frequencies will the driver of the second car hear? [514 Hz,545 Hz]
- An observer in a mountain town hears a train whistle and 3.0 s later hears the start of the echo from a cliff. The echo's frequency is 0.90 that of the sound heard directly.(a) how far is the train from the cliff? (b) how fast and in what direction is the train moving? [510 m, 17.9 m/s towards observer, train is between cliff and the observer]
- A transmitter sends out waves of frequency f and speed v.A target moves towards the transmitter at a speed u. Show that the frequency of the reflected waves received back at the transmitter is f(v+u)/(v-u). If u is much smaller than v show that this expression becomes f(1+2u/v).


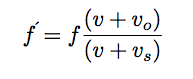 , where f' is the frequency measured by the observer, f is the frequency of the sound waves emitted by the source, v is the speed of sound and vo and vs are the velocities of the observer and source respectively. Note: Draw the arrow from the observer to the source. This is the positive direction for choosing the signs of the velocity vectors, vo and vs
, where f' is the frequency measured by the observer, f is the frequency of the sound waves emitted by the source, v is the speed of sound and vo and vs are the velocities of the observer and source respectively. Note: Draw the arrow from the observer to the source. This is the positive direction for choosing the signs of the velocity vectors, vo and vs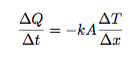 where the negative sign indicates that the heat flow ∆Q is from the high temperature end to the lower temperature end and the change in temperature ∆T is the final temperature minus the initial temperature. The thermal conductivity of the material is k, the cross sectional area that the heat flows through in a time ∆t is A and ∆x is the distance between the end points.
where the negative sign indicates that the heat flow ∆Q is from the high temperature end to the lower temperature end and the change in temperature ∆T is the final temperature minus the initial temperature. The thermal conductivity of the material is k, the cross sectional area that the heat flows through in a time ∆t is A and ∆x is the distance between the end points.